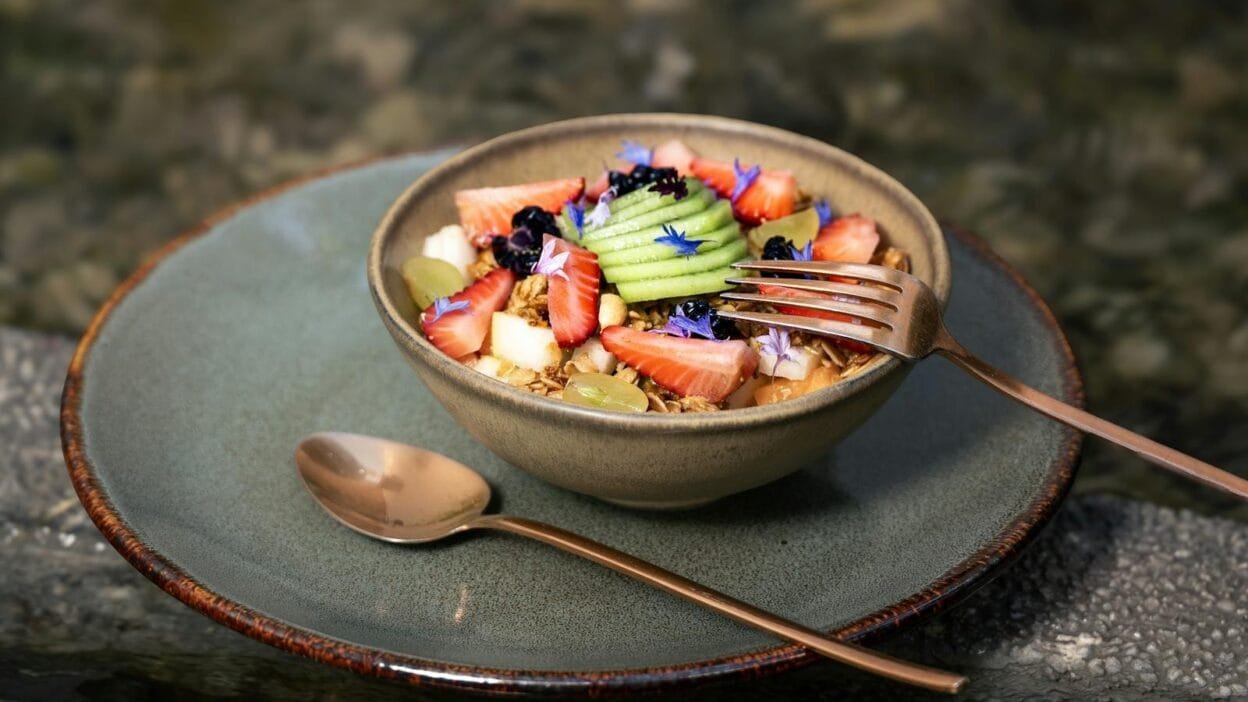
Diabetes Meal Planning is essential for individuals managing diabetes or seeking to stabilize their blood sugar levels. A well-structured meal plan transforms what may seem like a chore into a powerful tool for achieving consistent glucose control and overall well-being. By strategically planning your meals, you can proactively manage carbohydrate intake, prioritize nutrient-dense foods, and minimize unexpected blood sugar spikes.”
This article provides practical, easy-to-follow weekly and monthly meal planning guides designed specifically for blood sugar management. We’ll explore the benefits of structured meal planning, offering sample meal plans, customizable templates, and essential tips for making healthy and delicious choices that support your blood sugar goals. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or a seasoned expert, these resources will empower you to take control of your diet and pave the way for a healthier, more balanced life.
Introduction
Managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, especially for those at risk of or already living with diabetes. Meal planning plays a pivotal role in this journey, ensuring that your diet is balanced and nutritious. In this guide, we explore weekly and monthly meal planning strategies specifically designed for blood sugar control. We’ll walk you through understanding how your body manages sugar, why meal planning is essential, and how to create a personalized meal plan that fits your lifestyle. Whether you’re new to meal planning or looking to refine your approach, this guide provides practical insights and detailed strategies to help you stay on track.
Balanced meal planning not only stabilizes blood sugar levels but also boosts energy, improves mood, and supports long-term health. Throughout this article, you’ll discover step-by-step instructions and tips that can transform your approach to meal preparation. We emphasize a straightforward, optimistic tone, making complex nutritional information accessible at a Grade 7 reading level. So, let’s dive in and explore how a well-structured meal plan can empower you to take control of your health.
Understanding Blood Sugar Control
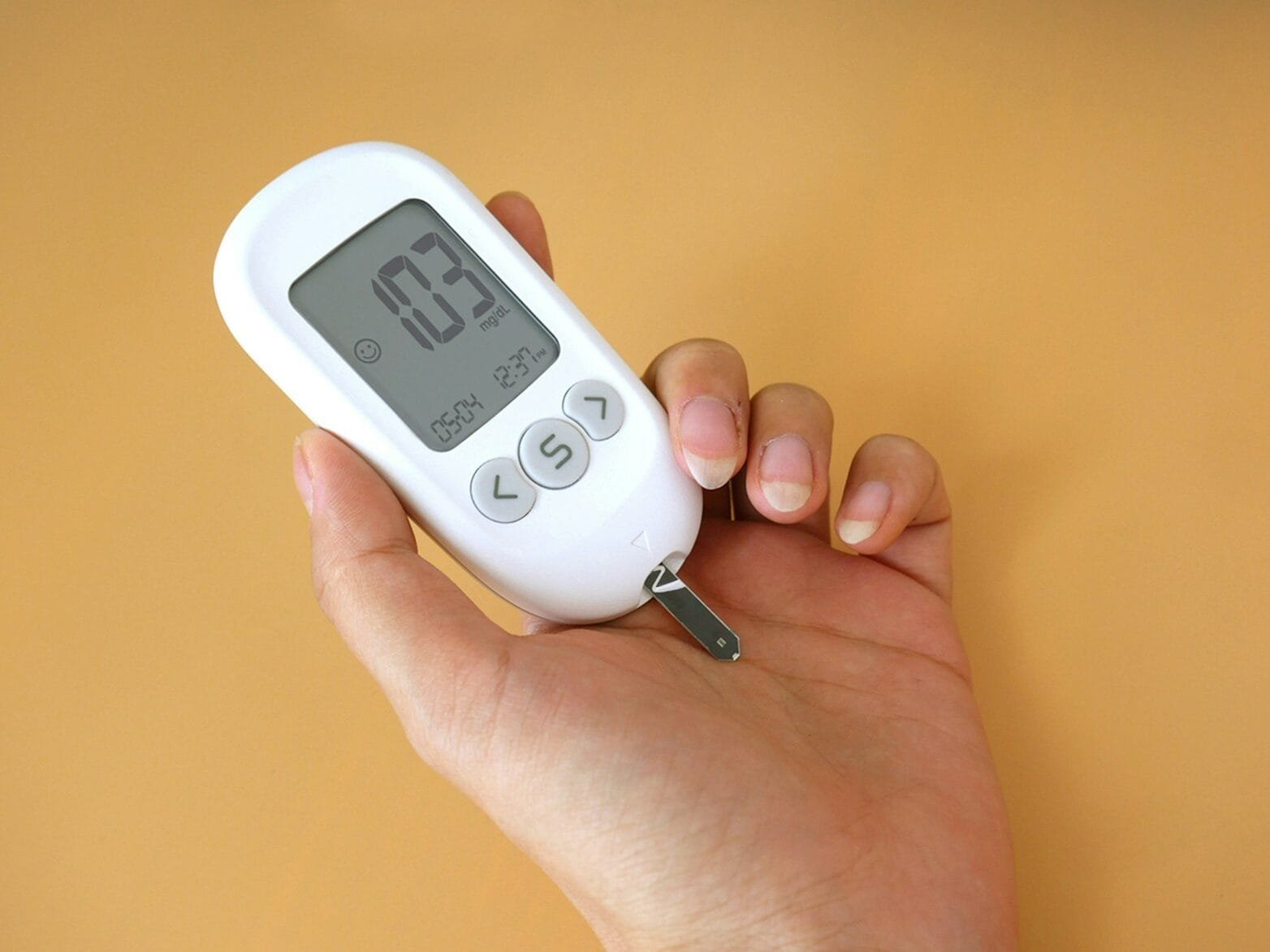
Blood sugar control refers to maintaining balanced levels of glucose in your bloodstream. This balance is essential because both high and low blood sugar levels can have significant health consequences. When you eat, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream and provides energy for your cells. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps cells absorb this glucose. However, if your body struggles with insulin production or sensitivity, you may experience fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
What is Blood Sugar Control?
Effective blood sugar control means keeping your glucose levels within a target range, thereby preventing spikes and crashes that can lead to serious complications. Conditions such as diabetes occur when your body cannot regulate blood sugar efficiently. Maintaining proper control is not only crucial for those with diabetes; it also benefits anyone aiming for a healthy lifestyle. Consistent blood sugar levels help you avoid energy dips, mood swings, and long-term damage to organs like the heart and kidneys.
In essence, blood sugar control is about balance. When you plan your meals carefully, you can help ensure that your body receives a steady supply of energy. This prevents the rapid shifts that might otherwise occur when you consume high-sugar foods or irregular meals. By understanding how food affects your glucose levels, you can make smarter dietary choices that support sustained energy and overall health.
The Role of Diet in Blood Sugar Levels
Your diet is one of the most influential factors in managing blood sugar. Foods rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats tend to slow down the absorption of sugar, leading to a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Conversely, refined carbohydrates and sugary snacks can cause quick spikes, overwhelming your system. Recognizing these effects is key to designing an effective meal plan. For instance, incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables can help maintain stability in your blood sugar levels.
Additionally, portion control is critical. Overeating—even healthy foods—can lead to higher blood sugar levels, as your body may struggle to process a large amount of glucose at once. Regular, balanced meals keep your metabolism working steadily, ensuring that you have the energy you need throughout the day. This understanding lays the foundation for why meal planning is such a vital tool in the quest for optimal blood sugar control.
With the knowledge of how various foods interact with your body, you can begin to design a meal plan that caters specifically to your needs. This involves not just what you eat, but also when and how you eat it. Scheduling meals at regular intervals can help your body anticipate and manage sugar intake more effectively, reducing the risk of dramatic spikes and crashes.
Meal planning is not about strict dieting or depriving yourself of foods you love; it’s about balance and smart choices. By learning about blood sugar control and the impact of your diet, you’re taking the first important steps towards a healthier lifestyle. With this understanding, you can now move on to explore why structured meal planning is so beneficial and how you can begin to craft your own meal plan.
The Importance of Diabetes Meal Planning
Meal planning is an indispensable tool for maintaining balanced blood sugar levels. When you organize your meals ahead of time, you reduce the risk of impulsive food choices that might spike your blood sugar. Planning your meals on a weekly or monthly basis provides structure, ensuring that every meal contributes to your health goals. Let’s break down the major benefits of meal planning and why it is essential for blood sugar control.
Benefits of Structured Meal Planning
Firstly, having a plan helps you incorporate a variety of foods that work together to keep your blood sugar stable. A balanced meal usually includes lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. When you pre-plan, you can ensure that each meal is balanced and contains the necessary nutrients. This prevents the temptation of reaching for high-sugar snacks when hunger strikes.
Another advantage is improved time management. Knowing what you’re going to eat throughout the week or month removes the daily stress of meal decisions. This can lead to more mindful eating, as you’re less likely to eat on the run or rely on processed foods that may adversely affect your blood sugar levels.
Moreover, meal planning is cost-effective. By creating a shopping list based on your meal plan, you avoid unnecessary purchases and reduce food waste. Budget-friendly meal planning ensures that you can maintain a healthy diet without overspending. This aspect is particularly important when you need to invest in higher-quality, nutrient-rich ingredients.
Weekly vs. Monthly Planning
One of the great things about meal planning is that it can be tailored to your lifestyle. Weekly plans allow for flexibility and adjustments as your schedule changes. They’re ideal for those who enjoy variety and want to incorporate seasonal produce. On the other hand, monthly plans provide a long-term strategy. They are beneficial if you’re looking to establish consistent habits and simplify shopping and preparation routines.
When you consider weekly and monthly planning together, you find that each approach offers unique advantages. Weekly planning is perfect for immediate needs and can be adjusted as circumstances change, while monthly planning provides an overarching framework that ensures you’re consistently on track with your health goals. Combining both strategies can give you the best of both worlds.
How Meal Planning Enhances Blood Sugar Control
Having a set meal schedule helps stabilize your blood sugar levels by preventing erratic eating patterns. When your body knows when to expect food, it can regulate insulin production more effectively. This regularity avoids the extreme fluctuations that occur with random snacking or skipped meals. Consistent meal timing is one of the most effective ways to manage blood sugar levels naturally.
Meal planning also gives you the opportunity to include a range of low-glycemic foods. These foods release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, preventing sharp spikes. By planning your meals, you ensure that you always have access to nutritious options that support steady blood sugar control. It also minimizes the likelihood of resorting to convenience foods, which often contain high levels of sugar and unhealthy fats.
Additionally, a well-thought-out meal plan allows you to monitor portion sizes more effectively. Overeating, even healthy foods, can lead to blood sugar surges. By measuring your servings in advance, you can maintain a balanced intake that aligns with your body’s needs.
In summary, the importance of meal planning cannot be overstated. It acts as the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle by simplifying decision-making, improving nutritional balance, and most importantly, stabilizing blood sugar levels. Once you embrace the benefits of meal planning, you can start creating a personalized plan that suits your unique lifestyle and dietary requirements.
Creating a Personalized Meal Plan
Developing a personalized meal plan is a dynamic process that begins with understanding your own nutritional needs. Everyone’s body is different, so a one-size-fits-all approach simply won’t work when it comes to managing blood sugar levels. With a tailored meal plan, you can balance carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in a way that keeps your glucose levels stable while still enjoying your favorite foods.
Assessing Nutritional Needs
The first step is to assess your nutritional needs. Consider your activity level, age, gender, and any medical conditions such as diabetes. A diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can slow the absorption of sugar, which helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Start by tracking your current eating habits for a week, noting the portions and types of food you consume. This log will help you identify areas for improvement and highlight patterns that may be contributing to blood sugar spikes.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can be highly beneficial at this stage. They can help you determine the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients needed to support your specific health goals. They might also suggest incorporating certain superfoods known for their blood sugar stabilizing properties, such as oats, nuts, leafy greens, and legumes.
Setting Achievable Goals
Once you have a clear picture of your nutritional needs, it’s time to set achievable goals. These goals should be realistic, measurable, and tailored to your lifestyle. For instance, you might aim to reduce your sugar intake by a certain percentage or increase your consumption of vegetables with each meal. Breaking down your long-term goal into weekly or even daily targets can make the process less overwhelming.
When setting these goals, keep in mind that progress is gradual. Celebrate small victories along the way—each healthy meal or successful grocery run is a step in the right direction. It’s also helpful to write down your goals and keep them visible. This constant reminder can motivate you to stick to your meal plan, even on days when you might feel tempted to stray.
Building Your Meal Framework
After assessing your needs and setting goals, you can begin constructing your meal framework. Start with your most important meals—breakfast, lunch, and dinner—and plan balanced options for each. Think about including a variety of proteins, whole grains, and a rainbow of fruits and vegetables. For instance, a balanced breakfast might include whole-grain toast, a serving of eggs, and a side of fresh fruit. This combination not only provides energy but also sets the tone for steady blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Meal prepping can be a game changer here. Dedicate time each week or month to prepare ingredients in bulk, such as chopping vegetables or cooking lean proteins. This practice makes it easier to stick to your meal plan, as you’ll have healthy options ready to go, reducing the likelihood of turning to processed or sugary alternatives.
Incorporating Flexibility
While structure is important, so is flexibility. Life happens, and there will be days when your plan needs tweaking. Allow room for spontaneity by including “flex meals” or planning for occasional dining out. The key is to balance indulgence with discipline. If you know you’re heading to a restaurant, look at the menu ahead of time and decide on healthier options.
Document your progress regularly and adjust your meal plan as necessary. A personalized plan is a living document that evolves with your needs. Keep track of how different foods affect your blood sugar and don’t be afraid to experiment with new recipes or ingredients. This continuous refinement ensures that your meal plan remains effective and enjoyable over the long term.
By taking the time to create a personalized meal plan, you’re investing in your future health. It’s about making conscious choices that support stable blood sugar levels while still leaving room for the pleasures of food. With a clear understanding of your nutritional needs, realistic goal-setting, and a flexible yet structured approach, you can build a meal plan that truly works for you.
Weekly Meal Planning Strategies for Blood Sugar Control
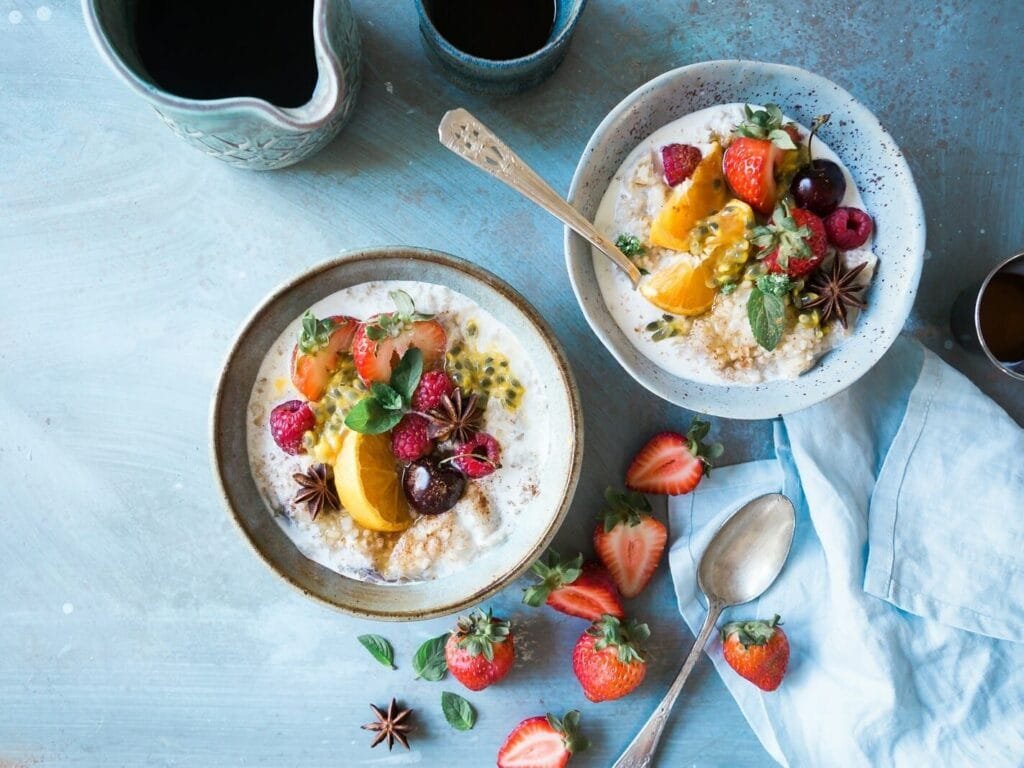

Weekly meal planning offers a balanced approach that combines structure with the flexibility to adapt to your evolving needs. When you plan your meals on a weekly basis, you’re setting yourself up for success by establishing a routine that helps manage blood sugar levels consistently. In this section, we’ll delve into effective strategies for weekly meal planning and provide actionable steps to create a balanced, nutrient-rich plan.
Establishing a Weekly Framework
Start by designating a day of the week—perhaps Sunday or Monday—as your meal-planning day. Use this time to review your schedule for the upcoming week. Consider any special events, work commitments, or social gatherings that might affect your meal routine. Once you have a clear picture of your week, draft a plan that includes breakfast, lunch, dinner, and healthy snacks. A well-rounded weekly plan ensures you’re not left scrambling for a quick fix, which often leads to choices that can spike blood sugar.
Creating a meal calendar is a great way to stay organized. You might use a digital calendar, a planner, or even a simple whiteboard in your kitchen. Map out each day’s meals, ensuring that you include a variety of foods to keep your diet interesting and nutritionally balanced. For example, you can plan a protein-rich breakfast on Mondays and switch to a lighter option like yogurt with berries on Tuesdays. Rotating these choices throughout the week not only prevents monotony but also ensures that your body receives a broad spectrum of nutrients.
Crafting Balanced Menus
The cornerstone of blood sugar control is a balanced meal. Each meal should ideally contain lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Consider incorporating foods like whole grains, beans, lean meats, and a variety of vegetables. A balanced plate not only helps stabilize blood sugar levels but also provides sustained energy throughout the day. For instance, a typical lunch might include grilled chicken, quinoa, steamed broccoli, and a drizzle of olive oil. Such combinations are not only delicious but also effective at preventing blood sugar spikes.
Meal prepping plays a vital role in weekly planning. Spend a few hours during your designated planning day to prepare ingredients in advance. Wash and chop vegetables, cook grains, or even prepare entire meals that can be stored in the refrigerator. This reduces the temptation to rely on quick, less healthy options when you’re pressed for time. Batch cooking also helps in managing portion sizes and ensures that you have balanced meals readily available.
Incorporating Variety and Flexibility
Even with a structured plan, it’s important to incorporate variety. Experiment with different recipes that meet your dietary requirements. Consider themes for different days of the week, such as Meatless Mondays or Fish Fridays, to keep your palate excited and your nutrition in check. Rotating your recipes can also prevent nutritional deficiencies and keep your blood sugar levels stable. Including seasonal fruits and vegetables is another excellent way to diversify your diet while enjoying fresh, local produce.
Flexibility is key when life throws unexpected changes your way. Build in backup options or quick-fix meals that are both healthy and satisfying. Having a few easy-to-prepare recipes on standby ensures you won’t stray from your plan during busy times. For example, a simple stir-fry made with pre-cut vegetables and tofu can be a lifesaver when you’re short on time but still want to eat healthily.
Tracking and Adjusting Your Plan
Maintaining a food diary or using a meal planning app can provide valuable insights into how your meals affect your blood sugar. Track your meals, note any deviations from your plan, and record how you feel after eating. This feedback loop allows you to adjust your plan based on real-life results. Over time, you’ll learn which foods help maintain stable blood sugar levels and which might cause unwanted spikes.
Remember, the goal of weekly meal planning is to create a sustainable routine that supports your health without feeling overly restrictive. Enjoy the process of planning and preparing your meals, and view it as an investment in your well-being. With consistency, you’ll find that your body adapts to regular, balanced meals, making it easier to manage blood sugar levels naturally.
By implementing these weekly meal planning strategies, you empower yourself to take control of your nutrition. The routine not only simplifies your daily decision-making but also provides a reliable framework for maintaining optimal blood sugar control. Stick with your plan, be open to adjustments, and celebrate the small victories along the way as you work towards a healthier lifestyle.
Monthly Meal Planning Strategies for Blood Sugar Control
While weekly planning offers immediate structure, monthly meal planning provides a long-term roadmap for sustained blood sugar management. By taking a broader view of your nutrition, you can align your dietary choices with seasonal availability, budget considerations, and overall health goals. In this section, we explore how to develop a monthly meal plan that is both flexible and robust enough to keep your blood sugar levels stable over time.
Setting Up Your Monthly Meal Blueprint
Begin by outlining your overall goals for the month. Reflect on the successes and challenges of previous meal plans and consider what changes you’d like to make. Are there specific nutritional targets you want to hit? Do you need to incorporate more variety or focus on particular meals? Establishing clear objectives at the outset ensures that your monthly plan is purposeful and aligned with your long-term health goals.
Create a master meal calendar for the month, including placeholders for all major meals and snacks. Use a large calendar or a digital tool that allows you to see the entire month at once. This bird’s-eye view helps you identify patterns, such as busy weeks when you might need more quick-prep meals, or weekends when you have time to experiment with new recipes. The goal is to craft a plan that is both structured and adaptable.
Integrating Seasonal and Budget-Friendly Foods
Monthly meal planning is an excellent opportunity to take advantage of seasonal produce. Seasonal fruits and vegetables are often more nutritious, flavorful, and cost-effective. Plan meals around what’s readily available in your local markets. For instance, incorporate fresh berries in the summer, hearty squashes in the fall, or crisp greens in the spring. This not only enhances your nutritional intake but also adds variety to your diet, which is essential for maintaining balanced blood sugar levels.
Budget considerations are also critical. When planning for the month, create a comprehensive grocery list that covers all your planned meals. Buying in bulk and taking advantage of sales can significantly reduce your food expenses. Consider preparing certain staples in larger quantities—like grains or legumes—that you can use throughout the month. This approach minimizes waste and ensures that you always have the ingredients needed to stick to your healthy eating plan.
Planning for Special Occasions and Flexibility
A monthly plan also needs to accommodate special occasions, dining out, or unexpected schedule changes. Identify days when you might be attending events or have less time to cook. For these days, plan for simple, grab-and-go meals that still adhere to your nutritional guidelines. Having a few “emergency” recipes or healthy snacks on hand can help you stay on track even when your routine is disrupted.
Flexibility is key in monthly planning. While it’s important to have a structured plan, be prepared to adjust it as needed. Keep a notebook or digital log where you can jot down any modifications, successes, or challenges. Over time, this record will become a valuable resource that you can reference to refine your planning process further.
Implementing Your Monthly Meal Plan
Once your monthly blueprint is ready, it’s time to put it into action. Dedicate a day at the start of the month to do a comprehensive grocery run. Organize your purchases based on your meal calendar, and consider using storage strategies that maintain the freshness of your ingredients. Meal prepping can also extend into your monthly plan—batch-cook proteins, prepare sauces, and chop vegetables that can be stored for the week ahead.
The beauty of monthly planning is that it gives you a chance to think ahead. You’re not only planning for individual meals but for an entire month of nutritional balance and blood sugar control. This holistic approach can alleviate the stress of daily decision-making and provide a clear roadmap for achieving your health goals.
By adopting these monthly meal planning strategies, you create a long-term framework that supports steady blood sugar control. The combination of strategic planning, seasonal adjustments, and built-in flexibility ensures that you can enjoy a variety of healthy, satisfying meals without the pressure of last-minute decisions.
Nutritional Guidelines for Blood Sugar Control
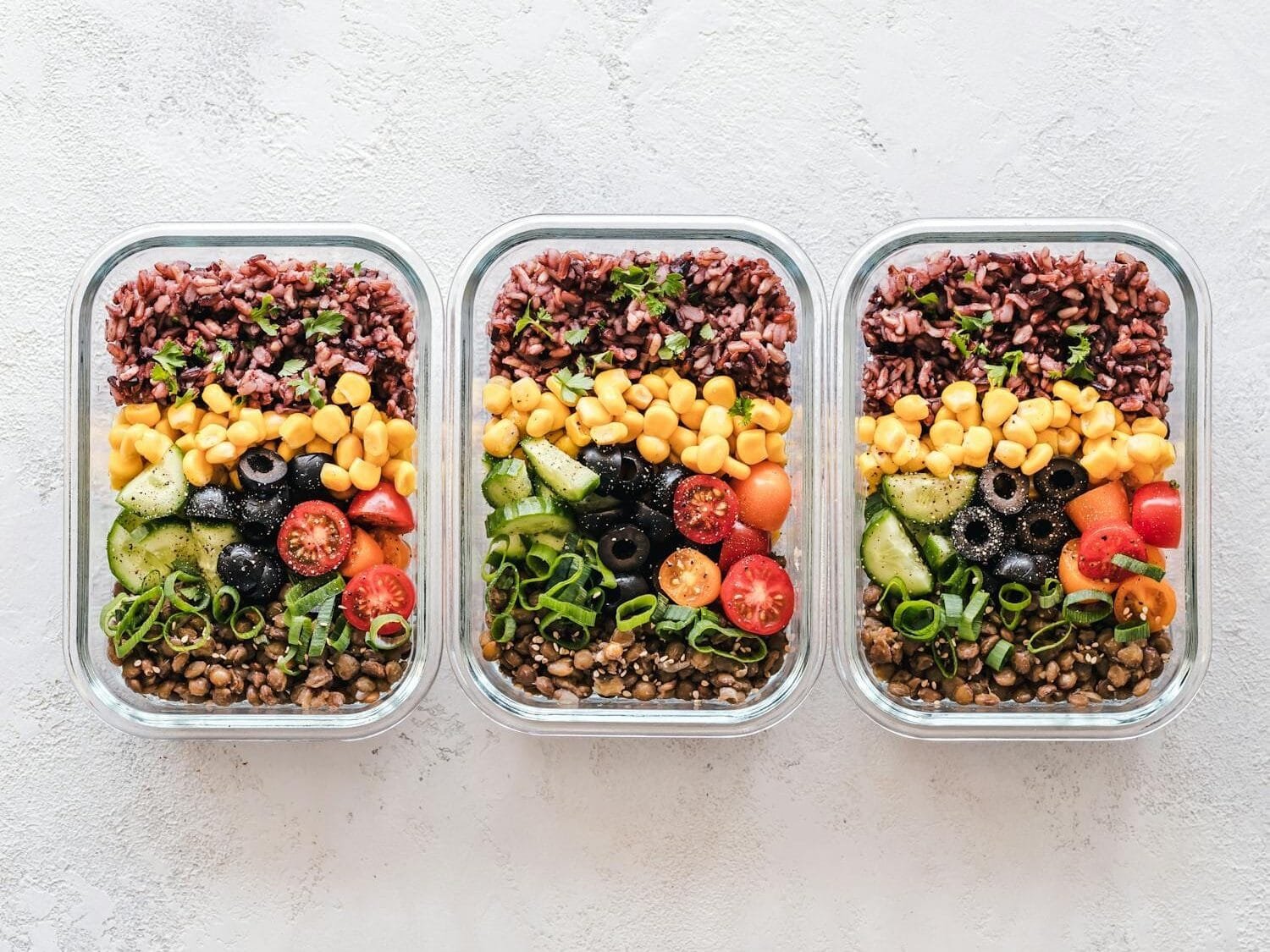

Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is deeply rooted in making smart dietary choices. In this section, we break down the nutritional guidelines that can help you create meals aimed at controlling blood sugar. From selecting the right carbohydrates to balancing macronutrients, these guidelines provide a roadmap for healthy eating.
A balanced diet for blood sugar control should include complex carbohydrates like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. These foods are digested more slowly, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose. Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes are also crucial. They not only support muscle maintenance but also help slow carbohydrate absorption. Healthy fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil play a supporting role in stabilizing blood sugar and enhancing the flavor of your meals.
Another important concept is the glycemic index (GI), which ranks carbohydrates based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are ideal for blood sugar control because they result in a slower, more gradual release of glucose. Integrating low-GI foods into your meal plan can significantly contribute to maintaining balanced levels throughout the day.
Portion control is equally important. Even nutrient-dense foods can cause blood sugar spikes if eaten in large quantities. Measuring your portions and using smaller plates can be effective strategies. Additionally, incorporating fiber-rich foods into every meal helps slow digestion and prolongs satiety. This combination not only keeps your blood sugar levels stable but also aids in weight management—a key factor in overall health.
Staying hydrated is often overlooked but plays a role in blood sugar regulation. Drinking plenty of water can help your body metabolize nutrients more efficiently, reducing the strain on your system. In practice, aim to include at least eight glasses of water daily, and adjust based on your activity level and climate.
Finally, mindful eating can make a big difference. Pay attention to your hunger cues and avoid overeating. Chew slowly, savor each bite, and listen to your body’s signals. This practice not only improves digestion but also helps you recognize when you’re truly full, preventing unnecessary calorie intake that could disrupt blood sugar balance.
By adhering to these nutritional guidelines, you create a solid foundation for meal planning that promotes blood sugar control. With each meal, you’re taking an active step toward improved health, ensuring that your body receives the right mix of nutrients to function optimally.
Practical Tips and Tricks
Even the best-laid meal plans can encounter bumps along the way. Practical tips and tricks help smooth the process and ensure that your strategies for blood sugar control remain effective and sustainable. Here are some actionable ideas to refine your approach:
- Keep It Simple: Start with a few basic recipes and gradually build your repertoire as you become more comfortable with meal planning.
- Use a Meal Planner App: Leverage technology to organize your meals, generate shopping lists, and even track how different foods affect your blood sugar.
- Batch Cooking: Dedicate time each week to prepare large portions of staple ingredients. This minimizes cooking time during busy days.
- Stay Organized: Use clear storage containers and label prepped ingredients to keep your kitchen efficient and reduce food waste.
- Adjust on the Fly: Life happens. If you need to deviate from your plan, have a list of healthy go-to options that can fill in the gaps.
- Learn from Experience: Keep a food diary to monitor how certain foods impact your blood sugar. Over time, you’ll be able to fine-tune your recipes and portion sizes.
These tips, combined with your personalized meal plan, create a comprehensive strategy for effective blood sugar control. The journey to improved health is all about consistent, small changes that add up over time. As you experiment with different recipes and strategies, remember to celebrate your progress—each healthy meal is a victory on your path to a better lifestyle.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the best time of day to eat for optimal blood sugar control?
A1: Eating at regular intervals—roughly every 3-4 hours—helps maintain steady blood sugar levels. A consistent meal schedule prevents spikes and dips, supporting better insulin regulation.
Q2: Can I still enjoy my favorite treats while managing blood sugar?
A2: Yes, moderation is key. Incorporate small portions of your favorite treats into your meal plan, and balance them with foods that have a low glycemic index. This helps minimize the impact on your blood sugar.
Q3: How do I adjust my meal plan if I exercise regularly?
A3: Physical activity increases your body’s demand for energy. If you exercise, you might need to adjust your carbohydrate intake and meal timing to ensure you have enough fuel without causing a blood sugar spike. Consult a nutritionist for personalized advice.
Q4: Are there any specific foods that can help improve blood sugar control?
A4: Foods high in fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, are excellent for stabilizing blood sugar. Additionally, lean proteins and healthy fats also contribute to a balanced diet that supports steady glucose levels.
Q5: How can meal prepping help in managing my blood sugar levels?
A5: Meal prepping reduces the likelihood of impulse eating and reliance on convenience foods, which can be high in sugar. By preparing balanced meals ahead of time, you ensure that you have nutritious options available, making it easier to maintain consistent blood sugar levels.
Q6: What should I do if my blood sugar levels remain unstable despite following a meal plan?
A6: If your blood sugar continues to be unpredictable, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can help adjust your plan, review your medications, and offer tailored advice to ensure your nutritional needs are met.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a structured meal plan is a powerful tool for controlling blood sugar levels and promoting overall health. Whether you opt for weekly or monthly planning, the key lies in understanding your body’s needs, setting realistic goals, and making mindful dietary choices. With balanced meals, proper portion sizes, and the incorporation of both lean proteins and complex carbohydrates, you can create a meal plan that supports steady blood sugar and enhances your quality of life.
Remember that flexibility and continuous adjustment are part of the process. Over time, as you fine-tune your plan based on personal feedback and nutritional guidelines, you’ll find that managing your blood sugar becomes a more natural, integrated part of your lifestyle. Embrace the journey, celebrate the small victories, and always keep your health goals in focus.
Additional Resources
For further reading and expert advice on managing blood sugar through nutrition, check out the resources at Mayo Clinic – Diabetes. Their comprehensive guides and expert insights can be an excellent complement to your meal planning journey.


