Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition characterized by the body’s diminished response to the hormone insulin. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy production. In individuals experiencing insulin resistance, cells become less responsive to insulin’s actions, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, this can result in an increase in insulin production as the pancreas attempts to compensate for the reduced cellular response.
The causes of insulin resistance are multifactorial. Genetic predisposition, obesity, physical inactivity, and poor dietary choices are primary contributors. Specifically, excess adipose tissue, particularly visceral fat, has been linked to increased inflammation and the secretion of certain hormones that can hinder insulin’s effectiveness. Additionally, dietary patterns rich in refined carbohydrates and sugars can exacerbate insulin resistance. Behavioral factors, including sedentary lifestyles, further perpetuate this condition, underscoring the importance of a holistic lifestyle approach in managing metabolic health.
Insulin resistance is a growing concern due to its strong association with various health complications. The condition not only serves as a precursor to type 2 diabetes but is also implicated in cardiovascular diseases, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and certain forms of cancer. As the prevalence of obesity and sedentary behaviors continues to rise, so does the incidence of insulin resistance, highlighting an urgent need for public health measures aimed at prevention and intervention. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of insulin resistance is essential for individuals aiming to improve their metabolic health and mitigate associated risks.
The Role of Minerals in Metabolism
Minerals are essential micronutrients that play a pivotal role in numerous metabolic processes within the human body. They are particularly crucial for the functioning of various enzymes and hormones that are responsible for regulating metabolism, including those involved in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. A balanced intake of minerals contributes to optimal metabolic function, which is vital for maintaining overall health and preventing metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance.
Among the key minerals that influence metabolic health, magnesium stands out due to its direct involvement in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Studies have shown that adequate levels of magnesium can enhance insulin action and help mitigate the effects of insulin resistance. Similarly, zinc is another mineral that plays an integral role in the synthesis and secretion of insulin, directly impacting glucose homeostasis in the body. The role of these micronutrients is often overlooked, yet their significance cannot be understated, as they contribute to the body’s ability to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, minerals such as chromium have garnered attention for their potential in improving insulin sensitivity. Chromium assists in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats, and its deficiency has been associated with increased insulin resistance. Incorporating mineral-rich foods into the diet can help prevent deficiencies and support metabolic health. Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent sources of these essential minerals, and their regular consumption can promote better metabolic outcomes.
Ultimately, a cohesive understanding of the role of minerals in metabolism highlights the importance of these micronutrients in sustaining energy balance and bodily functions. Ensuring adequate mineral intake is a fundamental aspect of nutritional health that can significantly impact overall wellness and metabolic efficacy.
Identifying the Key Mineral: Chromium
Chromium is a trace mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolic health, particularly in relation to insulin sensitivity and blood glucose regulation. It is found predominantly in the form of trivalent chromium, which is the biologically active form that the body can utilize effectively. This mineral has garnered attention for its ability to enhance the action of insulin, a hormone vital for glucose metabolism, thus helping to combat insulin resistance—a condition that has reached epidemic proportions globally.
The food sources rich in chromium include whole grains, meat, fruits, vegetables, and certain spices. While its concentration in specific foods can be relatively low, dietary patterns that include these chromium-rich foods can contribute significantly to its intake. It is essential to recognize that factors such as food processing can diminish chromium levels, potentially leading to deficiencies that may negatively impact metabolic health.
Historical context around chromium’s role in nutrition began to take shape in the early 1950s when it was first identified as a necessary dietary component. Subsequent research underscored the mineral’s significance in the regulation of glucose levels in the body. Over the decades, numerous studies have indicated a correlation between chromium supplementation and improved insulin sensitivity among individuals with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Modern dietary supplements frequently feature chromium in various forms, including chromium picolinate, which is thought to enhance absorption. The importance of chromium in metabolic processes cannot be overstated, as its adequate presence in the diet is linked to better management of blood sugar levels. Through optimal insulin function facilitated by chromium, individuals may experience improved metabolic outcomes, supporting overall health and wellness.
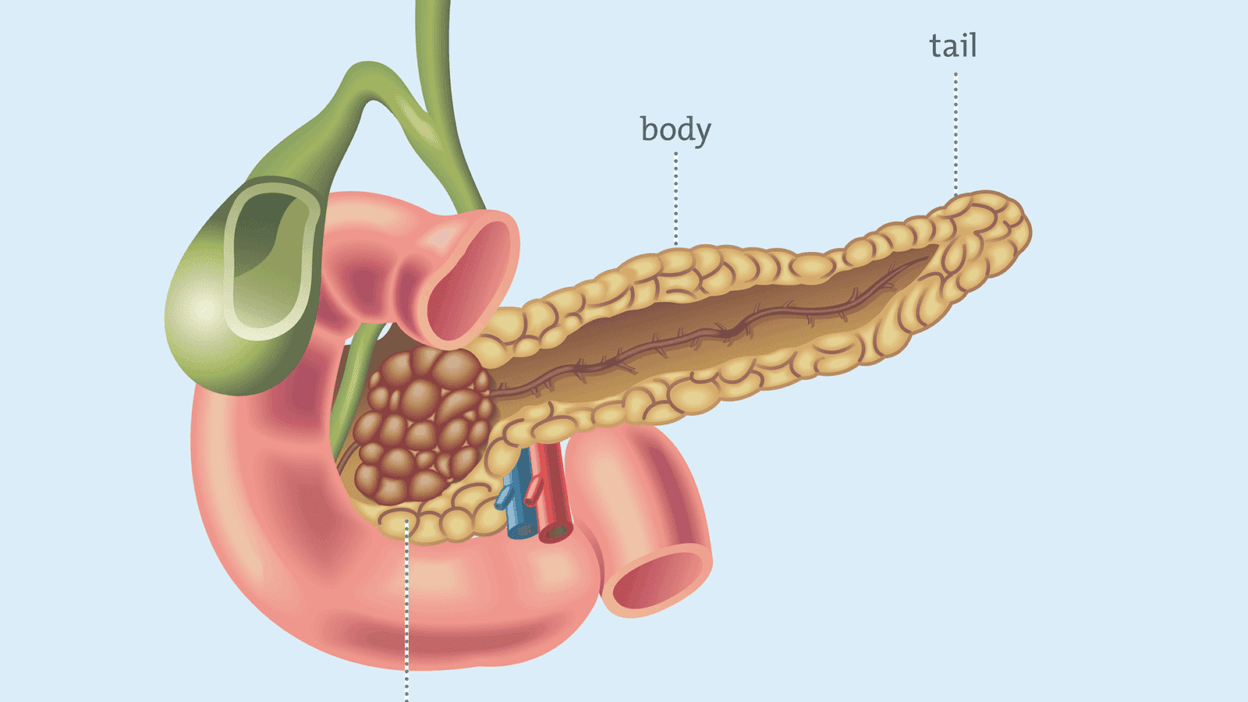
Mechanism of Chromium in Pancreatic Activation
Chromium is an essential trace mineral that plays a significant role in glucose metabolism and insulin action. At the cellular level, it is known to interact with the insulin receptor, enhancing its sensitivity and thereby facilitating better uptake of glucose by the cells. This interaction is primarily mediated through the chromodulin complex, a chromium-dependent protein that binds to insulin and increases its biological effectiveness. As a result, the pancreas is better able to produce insulin in response to elevated blood glucose levels, aiding in the management of metabolic health.
Furthermore, chromium has been shown to activate insulin receptors on various cell types, including muscle and fat tissues. This activation promotes the translocation of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) to the cell membrane, further enhancing glucose uptake. By improving the function of insulin receptors, chromium contributes to the reduction of insulin resistance, a common precursor to type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. The physiological effects of this mineral extend beyond just glucose metabolism; they also encompass lipid metabolism, where chromium influences cholesterol synthesis and the overall lipid profile.
Chromium’s role in modulating the activity of several enzymes involved in metabolic processes underscores its importance in promoting pancreatic health and function. Studies have indicated that adequate chromium levels can lead to a reduction in insulin resistance, supporting the pancreas’s capacity to regulate blood sugar. Moreover, this mineral may have antioxidative properties that further protect pancreatic beta cells from oxidative stress, which is often a contributing factor to insulin resistance. In conclusion, the intricate mechanisms by which chromium activates the pancreas highlight its potential as a beneficial nutrient in combatting metabolic health issues, particularly those associated with insulin resistance.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Chromium’s Benefits
Numerous clinical studies have underlined the efficacy of chromium supplementation in enhancing insulin sensitivity and supporting pancreatic function, thereby addressing issues related to insulin resistance. One pivotal study published in the “Journal of Nutrition” examined the effects of chromium picolinate on blood glucose control among individuals with type 2 diabetes. The research found that participants who supplemented with chromium exhibited improved glucose metabolism and significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels compared to those receiving a placebo. This highlights chromium’s potential role in metabolic health, particularly for those struggling with insulin resistance.
Moreover, a meta-analysis encompassing various randomized controlled trials reported a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c levels in subjects receiving chromium supplementation. HbA1c is a crucial marker for long-term blood sugar control, and its reduction signals improved insulin sensitivity. This analysis also pointed out that chromium demonstrated not only short-term benefits but sustained efficacy over extended periods of supplementation. However, results varied across different populations, indicating that effectiveness may depend on individual health conditions and chromium status prior to supplementation.
Despite these promising findings, some controversies exist regarding the dosage and formulation of chromium for optimal results. For instance, certain studies have suggested that high doses might lead to adverse effects, raising questions about the balance between efficacy and safety. Additionally, other research has not found significant benefits from chromium supplementation, particularly in non-diabetic populations, emphasizing the need for further investigation into who may benefit most from its use.
In light of this conflicting evidence, it is important for individuals to consult healthcare professionals before initiating chromium supplementation. Overall, while chromium poses potential advantages in improving insulin sensitivity and enhancing pancreatic health, ongoing research is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms involved and to resolve the discrepancies in clinical outcomes observed across diverse studies.
Dietary Sources of Chromium
Chromium is a trace mineral essential for maintaining metabolic health and plays a crucial role in regulating insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. To incorporate adequate amounts of this mineral into your diet, it is important to identify food sources that are rich in chromium. Foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and certain meats should be included in one’s daily diet for optimal chromium intake.
Whole grains, particularly oats, barley, and whole wheat bread, are good sources of chromium. These grains not only provide chromium but also offer dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and supports blood sugar stability. Fruits and vegetables such as broccoli, potatoes, and green beans are also rich in this vital mineral. They can be consumed raw or lightly steamed to preserve their nutrient content, thereby maximizing the availability of chromium.
In addition to fruits and vegetables, animal proteins can offer significant amounts of chromium. Meats like beef, poultry, and fish are effective choices for boosting dietary chromium levels. Individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets may find it beneficial to incorporate nuts, particularly almonds and walnuts, as well as legumes and brewer’s yeast to meet their chromium requirements.
The recommended daily intake of chromium varies slightly depending on age and sex, but generally, adult men are advised to consume 35 micrograms, while women should aim for 25 micrograms per day. When preparing foods, methods that involve minimal cooking time—such as steaming or microwaving—help retain the mineral content. Additionally, ensuring a diverse diet can further enhance chromium absorption, as the presence of certain nutrients can facilitate better utilization in the body. By consciously including these chromium-rich foods and adhering to recommended guidelines, individuals can take proactive steps in managing insulin resistance and improving their overall metabolic health.
Supplementation: Dosage and Safety Considerations
Chromium is available in various supplemental forms, including chromium picolinate, chromium chloride, and nicotinate chromium. These formulations differ in their bioavailability and effectiveness in promoting metabolic health and activating pancreatic function. Chromium picolinate is the most extensively studied form and is often preferred for its potential benefits in managing insulin resistance. It is essential to select a high-quality supplement, as the properties of different chromium forms may affect how well the body can absorb it.
The recommended dosage of chromium supplements typically ranges between 200 to 1000 micrograms per day, depending on the individual’s health status, age, and specific metabolic needs. It is crucial to adhere to the guidelines provided on the supplement packaging or those given by a healthcare professional. For individuals with diabetes, dosage may need to be adjusted based on blood glucose responses. Therefore, monitoring blood sugar levels and consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable before starting any chromium supplementation regimen.
While chromium is generally considered safe for most people, there are potential side effects, including gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, and skin reactions. In rare cases, excessive intake may lead to more severe health complications. Additionally, chromium can interact with certain medications, particularly those used to manage blood sugar levels, resulting in heightened hypoglycemic effects. Individuals with renal conditions or those who are pregnant or lactating should also approach supplementation with caution.
In conclusion, before incorporating chromium supplements into your health regimen, it is essential to engage in a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider. This dialogue ensures an informed decision regarding the right dosage, identifies potential interactions with existing medications, and assesses individual health conditions that may influence the suitability of supplementation. This comprehensive approach will help optimize metabolic health effectively and safely.
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Insulin Sensitivity

Improving insulin sensitivity is not solely reliant on supplementation; lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in optimizing metabolic health. Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective strategies. Moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can significantly enhance the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who incorporate aerobic exercise into their routine experience improved insulin sensitivity and better metabolic function.
Dietary strategies also contribute to enhanced insulin sensitivity. A balanced diet focusing on whole foods, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, is beneficial. Particular emphasis should be placed on minimizing processed foods that are high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats. Integrating foods rich in fiber, such as legumes and various fruits, can help improve glycemic control. Additionally, specific dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, have been linked to improved insulin sensitivity, highlighting the importance of nutrient quality over quantity.
Stress management techniques are equally critical for maintaining healthy insulin levels. Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, which is known to contribute to insulin resistance. Therefore, incorporating stress-reduction practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can prove advantageous. These techniques not only aid in reducing stress but also promote overall well-being, further supporting metabolic health.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes can yield significant benefits for insulin sensitivity. By combining physical activity, strategic dietary choices, and effective stress management techniques, individuals can create a holistic approach that complements the effects of chromium supplementation. This integrated strategy aims to empower individuals on their journey toward improved metabolic health and better management of insulin resistance.
Conclusion: The Path to Improved Metabolic Health
Addressing insulin resistance is a critical factor in achieving better metabolic health. This condition, characterized by the body’s diminished ability to respond to insulin, poses significant risks not only for diabetes but also for other metabolic disorders. The journey toward enhanced metabolic health requires understanding and managing blood sugar levels, which can be affected by various dietary and lifestyle choices.
Crucial to this endeavor is the mineral chromium, known for its pivotal role in supporting pancreatic function. Research has shown that chromium supplementation can improve insulin sensitivity and promote better glucose metabolism. By facilitating the action of insulin, chromium aids in preventing the disruptions that lead to insulin resistance, thus acting as a beneficial component in the management of blood sugar levels. Moreover, this mineral can enhance the pancreas’s ability to secrete insulin, essential for maintaining metabolic equilibrium.
A comprehensive approach to metabolic health should not only encompass supplementation with chromium but also integrate a focus on diet and lifestyle modifications. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods, rich in fiber and low in processed sugars, can significantly impact overall well-being. Regular physical activity, combined with mindfulness practices, can further enhance the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively, leading to lasting improvements in metabolic health.
In summary, addressing insulin resistance through a multifaceted strategy comprising chromium supplementation, dietary adjustments, and healthy lifestyle choices can significantly enhance pancreatic function and overall metabolic health. By prioritizing these elements, individuals can not only combat insulin resistance but also pave the way for a healthier future, marked by optimal metabolic functioning.