Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in numerous physiological processes, particularly in relation to insulin action and blood sugar regulation. The significance of magnesium cannot be overstated, especially for individuals managing diabetes, as studies have shown a strong connection between magnesium levels and metabolic health. It is estimated that a substantial percentage of people with diabetes have low levels of magnesium, which may hinder their ability to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Research indicates that magnesium facilitates the action of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose levels. When magnesium levels are adequate, insulin sensitivity improves, reducing the risk of insulin resistance, a common issue faced by those with diabetes. Additionally, magnesium is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and plays a crucial role in the process of converting glucose into energy. This interplay emphasizes the necessity of incorporating magnesium high foods into the diets of diabetics.
Moreover, magnesium deficiency has been linked to several complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, elevated blood pressure, and neuropathy. In fact, studies suggest that individuals with higher dietary intake of magnesium, particularly from foods high in magnesium, show improved overall health outcomes. These findings highlight the importance of consuming foods that are high in magnesium to mitigate potential risks associated with diabetes.
Therefore, understanding the relationship between magnesium levels and diabetes management is imperative. By prioritizing magnesium high foods, individuals with diabetes can enhance their metabolic health and improve insulin function. The upcoming sections will delve into specific magnesium high foods that can beneficially influence blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Why Magnesium is Essential for Diabetics
Magnesium deficiency is a prevalent concern within the diabetic population, often overlooked but critical to overall health. Studies indicate that individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of experiencing low magnesium levels, primarily due to insulin resistance and the increased renal excretion of magnesium, which can result from prolonged hyperglycemia. This dual challenge creates a cycle where a lack of magnesium can further aggravate insulin resistance, ultimately complicating diabetes management.
The symptoms of magnesium deficiency can vary but commonly include muscle cramps, fatigue, and weakness. Some individuals may experience mood changes or a general sense of malaise, all of which could significantly impact a diabetic individual’s quality of life. Additionally, low magnesium levels have been linked to various metabolic disturbances, including elevated blood sugar levels and poor glycemic control. These issues highlight the importance of magnesium high foods in the diets of those with diabetes.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake through natural dietary sources can help mitigate some of the adverse effects related to deficiency. Incorporating foods high in magnesium can aid in regulating blood sugar levels, thereby offering a dual benefit for diabetics seeking to improve their overall health. Several foods that are high in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, should be emphasized as part of a balanced diet. Several studies support these claims, showing that increased magnesium consumption is associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
For further insights on the impact of magnesium deficiency in diabetic individuals, reputable external studies provide valuable data that illustrate the necessity of maintaining adequate levels through dietary choices rich in magnesium. By prioritizing magnesium high foods, diabetics can play a proactive role in their health management.
How Much Magnesium Do Diabetics Need Daily?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium may vary based on individual needs, but for most adults, the daily requirements are:
| Group | RDA (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Adult Men (19-30) | 400 |
| Adult Women (19-30) | 310 |
| Pregnant Women | 350 |
| Older Adults (31+) | 420 for men; 320 for women |
Diabetics may require slightly higher intake to support optimal blood sugar control, but it’s best to consult a healthcare professional.
Benefits of Consuming Magnesium High Foods for Diabetics

Magnesium plays a crucial role in the metabolic processes that affect individuals with diabetes. Scientific studies have demonstrated that adequate magnesium levels enhance insulin sensitivity, which is particularly beneficial for those managing type 2 diabetes. Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively the body responds to insulin, and improved sensitivity means that the body can utilize glucose more efficiently, thereby aiding in better blood glucose control. Magnesium participates in over 300 enzymatic reactions, many of which are integral to carbohydrate metabolism. Consequently, magnesium high foods can significantly influence blood sugar levels.
Moreover, consumption of foods high in magnesium has been linked to a reduced risk of developing complications associated with diabetes. Research has indicated that individuals with higher magnesium intake have lower incidences of diabetic complications, such as nephropathy and retinopathy. The mineral helps regulate blood pressure, which is particularly important as diabetics are at increased risk for hypertension. By including magnesium high foods in their diet, diabetics not only manage their blood sugar but also lower their chances of experiencing adverse health outcomes.
Cardiovascular health is another area where magnesium shines in its benefits for individuals with diabetes. Studies have shown that diets rich in magnesium are associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. Magnesium aids in maintaining normal heart rhythms and contributes to the health of blood vessels, reducing the likelihood of conditions like atherosclerosis, which is common in diabetics. By prioritizing foods that are high in magnesium, individuals can enhance their heart health and overall well-being, leading to a healthier lifestyle.
In conclusion, the inclusion of magnesium high foods in the daily diet can provide numerous benefits for diabetics. From improved insulin sensitivity to enhanced cardiovascular health, the advantages of magnesium are backed by scientific evidence, making it a vital nutrient for those managing diabetes.
Top 15 Magnesium High Foods for Diabetics
Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, especially for diabetics. A consistent intake of magnesium high foods can aid in blood sugar control and improve insulin sensitivity. Below are 15 foods that are high in magnesium and can easily be incorporated into a diabetic-friendly diet.
1. Dark Leafy Greens
Rich in magnesium and low in carbs, leafy greens like spinach and kale are ideal choices for diabetics aiming to manage their blood sugar levels. Spinach, in particular, stands out as a nutrient powerhouse, offering about 157 mg of magnesium per cooked cup. This essential mineral supports insulin sensitivity and helps regulate glucose levels, making it a vital addition to a diabetic-friendly diet. Kale, another excellent option, provides similar benefits along with an array of antioxidants that promote overall health. Incorporating these greens into salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes is an easy and delicious way to boost your magnesium intake while keeping carb counts in check.
2. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, cashews, and sunflower seeds are excellent sources of magnesium, making them a smart choice for a diabetes-friendly diet. These nutrient-dense snacks not only provide a healthy dose of magnesium but also offer beneficial fats, protein, and fiber to support stable blood sugar levels. For instance, a 1-ounce serving of almonds delivers approximately 80 mg of magnesium, contributing significantly to your daily intake. Cashews and sunflower seeds also add variety and flavor while ensuring you get essential nutrients. Whether enjoyed on their own, sprinkled over salads, or added to trail mix, these magnesium-rich foods are both convenient and nutritious.
3. Whole Grains
Quinoa and brown rice are fantastic options for stabilizing blood sugar while providing a generous amount of magnesium. Quinoa, in particular, stands out as a nutrient-rich grain alternative, offering approximately 118 mg of magnesium per cooked cup. It’s also a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids, which makes it especially beneficial for those managing diabetes. Brown rice, with its high fiber content, helps maintain steady glucose levels and supports digestion. Incorporating these magnesium-rich foods into your meals, such as in grain bowls, stir-fries, or side dishes, is an easy and delicious way to boost nutrition and promote overall health.
4. Fatty Fish
Salmon, mackerel, and tuna are not only rich in magnesium but also packed with heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, making them an excellent choice for a balanced, diabetes-friendly diet. These nutrient-dense fish support healthy blood sugar levels while promoting cardiovascular health, which is especially important for individuals with diabetes. The combination of magnesium and omega-3s helps reduce inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower the risk of heart disease. Enjoy these fish grilled, baked, or added to salads for a delicious way to incorporate both magnesium and essential nutrients into your meals.
5. Legumes
Chickpeas, lentils, and black beans are excellent sources of magnesium and are highly beneficial for regulating blood sugar levels. These versatile legumes are rich in fiber and protein, which help slow digestion and promote steady glucose levels. Black beans, in particular, stand out with approximately 120 mg of magnesium per cooked cup, making them a great addition to a diabetes-friendly diet. Whether added to soups, salads, stews, or grain bowls, these legumes provide a satisfying and nutrient-dense way to incorporate magnesium into your meals while supporting overall health and blood sugar management.
6. Bananas
While higher in natural sugars, bananas can still be a beneficial addition to a diabetes-friendly diet when consumed in moderation. A medium-sized banana provides approximately 32 mg of magnesium, along with essential nutrients like potassium and fiber. The fiber content helps slow down the absorption of natural sugars, supporting more stable blood sugar levels. Bananas can be enjoyed on their own, sliced into oatmeal, or blended into a smoothie for a quick and nutritious snack that contributes to your magnesium intake while offering a boost of energy.
7. Avocados
A single avocado contains approximately 58 mg of magnesium, an essential mineral that supports numerous bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function, blood sugar regulation, and bone health. In addition to magnesium, avocados are rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, which can help improve cholesterol levels and support cardiovascular health. For diabetics, the combination of healthy fats and magnesium makes avocados an excellent choice, as they can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall well-being.
8. Dark Chocolate
High-quality dark chocolate, containing 70-85% cocoa, is an unexpected yet excellent source of magnesium, offering about 64 mg per ounce. Magnesium plays a vital role in maintaining muscle function, heart health, and blood sugar regulation. For the best benefits, choose unsweetened or minimally sweetened varieties, as these are lower in added sugars and provide a richer concentration of antioxidants, such as flavonoids, which support cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation. Enjoying dark chocolate in moderation can be a delicious way to boost your magnesium intake while promoting overall health.
9. Tofu
Tofu is an excellent plant-based protein source that offers a wealth of nutritional benefits. A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving provides approximately 53 mg of magnesium, an essential mineral that supports muscle function, bone health, and blood sugar regulation. In addition to magnesium, tofu is rich in high-quality protein and contains essential amino acids, making it a versatile and nutrient-dense food. Its low carbohydrate content and heart-healthy unsaturated fats make tofu an ideal choice for those managing diabetes or aiming to maintain a balanced diet. Whether stir-fried, grilled, or added to soups and salads, tofu is a delicious and healthful addition to any meal.
10. Yogurt
Low-fat or Greek yogurt is a nutritious addition to a balanced diet, providing approximately 42 mg of magnesium per cup. Magnesium is essential for energy production, nerve function, and maintaining healthy blood pressure. In addition to its magnesium content, yogurt is an excellent source of protein, calcium, and probiotics—beneficial bacteria that promote a healthy gut microbiome, improve digestion, and support immune function. Opting for plain, unsweetened varieties ensures you avoid added sugars while reaping the full health benefits. Enjoy yogurt on its own, as a smoothie base, or paired with fresh fruit and nuts for a wholesome, nutrient-packed snack.
11. Pumpkin Seeds
Pumpkin seeds are a nutrient-dense snack, delivering an impressive 168 mg of magnesium per ounce, making them one of the richest natural sources of this essential mineral. Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle function, nerve health, and energy production while also supporting heart and bone health. In addition to magnesium, pumpkin seeds are packed with antioxidants, healthy fats, protein, and other essential nutrients like zinc and iron. They can be enjoyed on their own, sprinkled over salads, blended into smoothies, or incorporated into baked goods, providing a crunchy and nutritious boost to your diet.
12. Almonds
A handful of almonds, approximately one ounce or about 23 nuts, provides 76 mg of magnesium, making them an excellent choice for boosting your intake of this vital mineral. Magnesium is essential for energy production, muscle and nerve function, and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Beyond their magnesium content, almonds are rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, protein, and fiber, which help promote satiety and curb hunger between meals. They also contain vitamin E and antioxidants that support skin health and combat oxidative stress. Enjoy almonds as a convenient snack, or add them to oatmeal, yogurt, or salads for a nutritious crunch.
13. Spinach
Cooked spinach is a powerhouse of nutrition, providing 157 mg of magnesium per cup. This leafy green is an excellent choice for supporting muscle and nerve function, maintaining healthy blood pressure, and promoting strong bones, thanks to its high magnesium content. In addition to magnesium, spinach is rich in iron, calcium, potassium, and vitamins A, C, and K, making it a nutrient-dense option for overall health. Its versatility allows it to be easily incorporated into various dishes, such as soups, stews, omelets, or as a side dish. Adding cooked spinach to your meals is a simple and delicious way to boost your nutrient intake.
14. Black Beans
Black beans are a nutritious and versatile legume, offering 120 mg of magnesium per cooked cup. This essential mineral plays a key role in energy production, nerve function, and blood pressure regulation. For individuals managing blood sugar, black beans are especially beneficial, as their high fiber and protein content help slow the absorption of glucose, promoting steady blood sugar levels. In addition to magnesium, black beans are rich in iron, folate, and antioxidants, which support heart health and overall well-being. Enjoy black beans in soups, salads, stews, or as a hearty side dish to enhance your meals with both flavor and nutrition.
15. Edamame
Edamame, or young soybeans, is a nutrient-rich snack that provides 99 mg of magnesium per cooked cup. This magnesium boost supports muscle function, energy production, and healthy blood sugar regulation. In addition to magnesium, edamame is packed with plant-based protein, fiber, and essential vitamins like folate and vitamin K, making it a satisfying and balanced choice for snacking. Its low glycemic index and healthy fat content make it particularly beneficial for managing blood sugar levels. Whether enjoyed plain, lightly salted, or seasoned with spices, edamame is a delicious and convenient way to fuel your body with essential nutrients.
Potential Risks of Excess Magnesium Intake
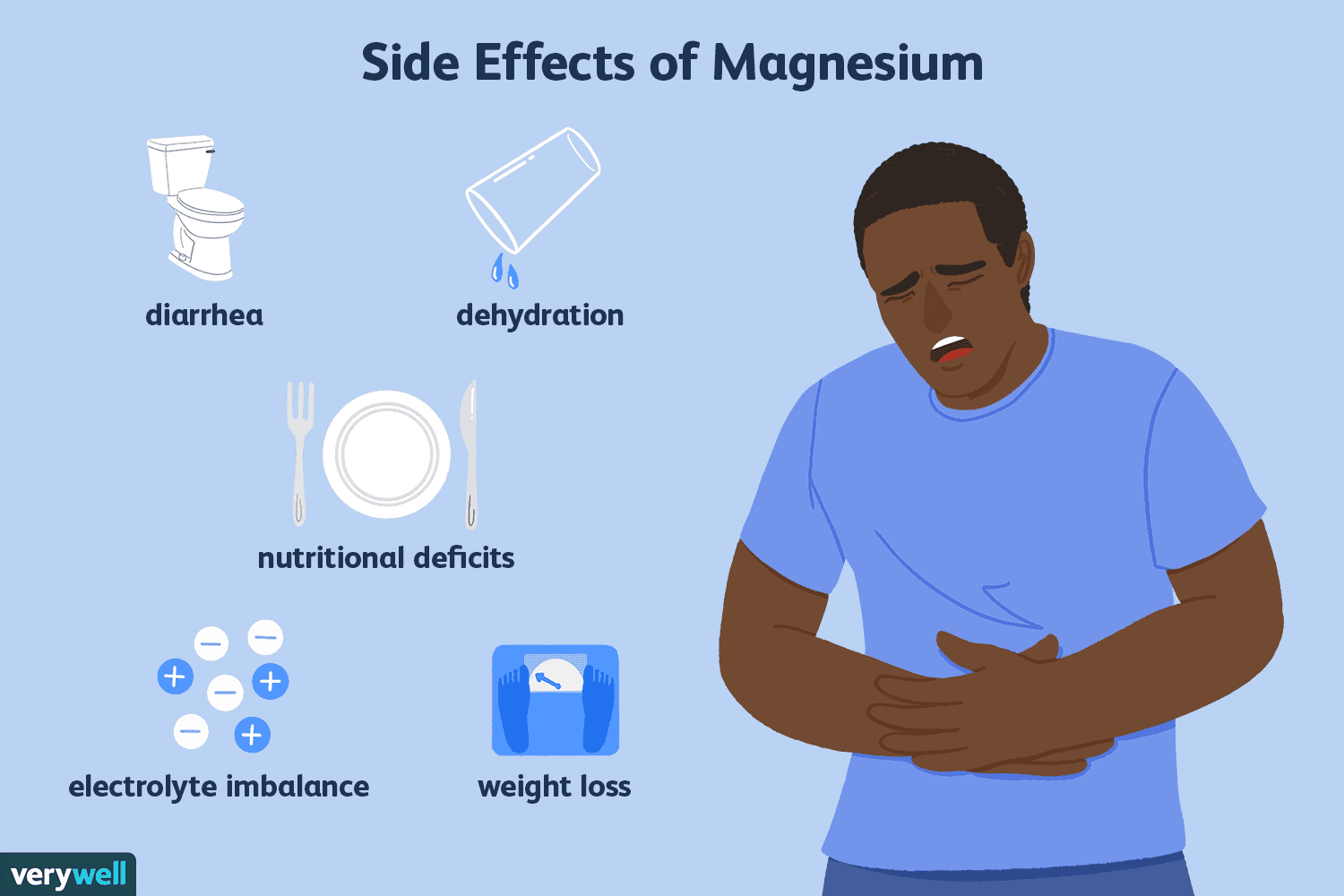
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and blood sugar regulation. While magnesium high foods offer numerous health benefits, it is important to recognize the potential risks associated with excessive intake, especially when derived from supplements rather than naturally occurring sources. Foods that are high in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, typically do not pose the same risks, as they are unlikely to lead to overconsumption.
When taken in large doses, particularly in supplement form, magnesium can lead to toxicity. Symptoms of magnesium overdose may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea. More severe reactions could result in a slowdown of heart rate, low blood pressure, respiratory distress, and in extreme cases, cardiac arrest. Individuals with existing kidney conditions should exercise caution, as their bodies may struggle to effectively eliminate excess magnesium.
To avoid the risks associated with too much magnesium, health organizations, including the National Institutes of Health (NIH), recommend a balanced approach to intake. Adults should consume magnesium from both dietary sources and supplements as needed, aiming to stay within the established daily adequate intake values. For men, the recommended dietary allowance is about 400-420 mg per day, while women typically require 310-320 mg per day. For those particularly concerned about their magnesium levels, consulting with a healthcare professional can provide tailored advice suited to one’s individual health needs.
In conclusion, while magnesium high foods are beneficial for health, awareness of the potential risks of excessive intake is necessary. Ensuring a balanced diet and adhering to recommended guidelines can help in reaping the advantages of magnesium without undue risk to health.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
When making significant dietary changes or considering supplementation, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals. The unique needs of individuals, especially those managing diabetes, call for personalized dietary plans that take various factors into account. Each person has different responses to foods and nutrients; therefore, a one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective. For those exploring magnesium high foods, such as dark leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, it becomes even more critical to evaluate how these choices fit within their overall health strategy.
Healthcare providers can offer valuable insights into the importance of maintaining adequate magnesium levels and how they pertain specifically to diabetic care. Individuals with diabetes often face various complications, including potential magnesium deficiencies, which can impact glucose control and overall health. A thorough discussion with a doctor can help assess current magnesium status and determine whether dietary changes incorporating foods that are high in magnesium might be beneficial. This level of guidance ensures that any adjustments in diet align with personal health goals and existing medical conditions.
It is advisable for individuals to actively engage with their healthcare teams regarding any new dietary initiatives, particularly when introducing foods high on magnesium or considering supplements. By discussing their interest in increasing magnesium intake and inquiring about suitable foods high in magnesium, patients can work collaboratively with their providers to optimize their nutritional approach.
In conclusion, consulting healthcare professionals before making dietary changes is crucial, especially for diabetics looking to incorporate magnesium high foods. This practice not only personalizes health plans but also enhances overall well-being, paving the way for informed and effective nutrition. Such proactive engagement ensures that dietary decisions support their health needs comprehensively.
Easy Recipes to Incorporate Magnesium High Foods for Diabetics
Managing diabetes becomes more manageable with a well-balanced diet, and including magnesium high foods is a smart and effective choice. Magnesium is essential for controlling blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and supporting overall health. Fortunately, there are many simple and delicious ways to add these foods to your daily meals. Recipes like spinach and almond salads, quinoa and black bean bowls, or roasted salmon with pumpkin seeds offer a delightful blend of flavors and vital nutrients. Additionally, healthy snacks like dark chocolate or smoothies with bananas and chia seeds provide quick, magnesium-packed options to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Delicious Magnesium High Foods Recipes
Spinach and Avocado Salad:
Start with a bed of fresh spinach leaves, rich in magnesium, and add creamy avocado slices for healthy fats. Sprinkle in crunchy pumpkin seeds for an extra magnesium boost. Drizzle the salad with extra virgin olive oil and fresh lemon juice, then finish with a pinch of salt and cracked black pepper for a simple yet nutrient-packed dish.
Quinoa and Black Bean Bowl:
Cook a batch of fluffy quinoa, a magnesium powerhouse, and mix it with seasoned black beans. Roast colorful vegetables like zucchini, bell peppers, and sweet potatoes, and layer them over the quinoa. Top with a dollop of Greek yogurt, a squeeze of lime, and freshly chopped cilantro for a filling, balanced meal.
Roasted Salmon with Sesame and Pumpkin Seeds:
Season salmon fillets with a touch of olive oil, garlic, and lemon, then coat with a mixture of sesame and pumpkin seeds before baking. These seeds add both texture and a significant dose of magnesium, while the salmon provides heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
Dark Chocolate Almond Bark:
Melt dark chocolate (preferably 70-85% cocoa) and mix it with roasted almonds, sunflower seeds, and a pinch of sea salt. Spread the mixture on a lined baking sheet and allow it to harden in the refrigerator. Break into pieces for a delectable magnesium-rich snack.
By incorporating these easy and flavorful recipes featuring magnesium high foods into your diet, you can enjoy a variety of nutrient-dense meals while effectively supporting diabetes management. Eating healthfully doesn’t have to be complicated—it can be both simple and delicious!
FAQs About Magnesium and Diabetes
How does magnesium benefit diabetics?
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in enhancing insulin sensitivity, which helps the body’s cells respond more effectively to insulin. It also aids in regulating blood sugar levels by supporting the activity of enzymes involved in glucose metabolism, ensuring better glycemic control for individuals with diabetes.
Can diabetics get enough magnesium from food alone?
Yes, a balanced diet rich in magnesium can effectively meet the daily requirements for most diabetics, ensuring they receive adequate nutrients to support optimal blood sugar control, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain overall metabolic health.
What are the risks of consuming too much magnesium?
Excessive magnesium from supplements may cause diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. In severe cases, taking too much magnesium can also lead to more serious health issues, such as irregular heartbeat or low blood pressure, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney problems. It’s crucial to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation.
Are magnesium supplements necessary for diabetics?
Supplements may be needed for those with deficiencies to restore optimal magnesium levels, especially in cases of severe depletion. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider first to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure it does not interact with other medications or medical conditions.
Which magnesium high foods help regulate blood sugar?
Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and legumes are particularly beneficial for managing blood sugar levels due to their high magnesium content and other vital nutrients. These foods help improve insulin sensitivity, stabilize glucose levels, and provide essential vitamins and fiber to promote overall metabolic health.
How does cooking affect magnesium content?
Boiling can significantly decrease magnesium levels in foods, as the mineral leaches into the water during cooking. To retain the most magnesium, opt for cooking methods like steaming or roasting, which help preserve the nutrient content while enhancing the natural flavors of the food.
Embracing a magnesium high foods for Diabetes Management
Incorporating magnesium high foods into your daily diet can play a vital role in managing diabetes and improving overall health. Magnesium is an essential mineral that not only supports various bodily functions but also aids in regulating blood sugar levels. As we have discussed, foods that are high in magnesium such as leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains can greatly contribute to a balanced diet. By understanding and integrating these foods into your meals, you can potentially enhance your insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
The significance of magnesium high foods in diabetes management cannot be overstated. Research indicates that individuals with diabetes often have lower magnesium levels, which may exacerbate insulin resistance. For this reason, it becomes imperative to prioritize the consumption of foods high in magnesium. While implementing dietary changes, it is advisable to consult with healthcare providers or nutritionists who can tailor a plan that is suitable for your specific health needs. They can guide you on appropriate portion sizes and combinations of magnesium high foods that suit your lifestyle.
Moreover, sharing your journey with friends, family, or online communities can provide additional motivation and support. As you explore new recipes and meal options that are enriched with magnesium, consider documenting your experiences. Your insights may inspire others to also embrace a diet abundant in foods that are high in magnesium. Together, we can foster a community that prioritizes health and well-being through informed dietary choices. Take this opportunity to make positive changes that benefit your health, and remember that every small step counts in the journey towards effective diabetes management.